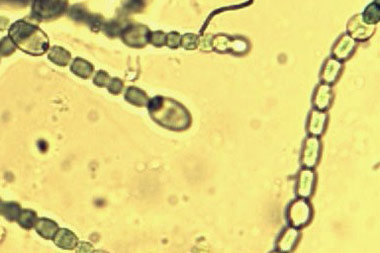
 Alpha Analytical is now identifying and enumerating water matrices for algae speciation using various forms of microscopy.
Alpha Analytical is now identifying and enumerating water matrices for algae speciation using various forms of microscopy.
The identification and enumeration of algae in lakes and other freshwater ecosystems provides a simple, reliable, and cost-effective measure of water quality. As the major primary producers in aquatic ecosystems, algae play an important role in energy flow and nutrient cycling. Algal blooms may indicate excessive nutrient loading, pollution, or other environmental problems. Determination of the numbers and types of algae present in a water body is useful in environmental monitoring programs and impairment assessments, because these characteristics respond quickly to changes in water chemistry. Because of their short life cycle, changes in water quality are often reflected by changes in the algal community within a few days or weeks.
In addition to their value in biological monitoring programs, some algae can become problematic. Excessive algal growth can cause a number of water-quality problems, including: bad taste and odor, de-oxygenation of water, and fish kills. Some blooms are toxic to wildlife and humans. Clogged pipes, filters, or screens in water and wastewater treatment plants are other problems caused by excessive algal growth, resulting in increased costs to water utilities and municipalities. Correct identification of target species is critical when determining a management strategy.
 Alpha Analytical is now supporting drinking
Alpha Analytical is now supporting drinking Using EPA method 1631, we’re analyzing aqueous samples for TOTAL inorganic mercury down to 0.5 part per trillion levels by oxidation, purge & trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. In order to speciate and look for ORGANIC or methyl mercury down to 0.05 par per trillion levels, we have installed a new technology Tekran distillation and instrument unit calibrated to analyze aqueous samples by method EPA 1630 using a distillation, ethylating, purge & trap, gas chromatography and cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry.
Using EPA method 1631, we’re analyzing aqueous samples for TOTAL inorganic mercury down to 0.5 part per trillion levels by oxidation, purge & trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. In order to speciate and look for ORGANIC or methyl mercury down to 0.05 par per trillion levels, we have installed a new technology Tekran distillation and instrument unit calibrated to analyze aqueous samples by method EPA 1630 using a distillation, ethylating, purge & trap, gas chromatography and cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Alpha Analytical is now certified to analyze water matrices for Perchlorate by EPA method 314.0.
Alpha Analytical is now certified to analyze water matrices for Perchlorate by EPA method 314.0. Alpha Analytical is now identifying and enumerating water matrices for algae speciation using various forms of microscopy.
Alpha Analytical is now identifying and enumerating water matrices for algae speciation using various forms of microscopy.  Alpha Analytical is analyizing wastewater for production chemicals for the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.
Alpha Analytical is analyizing wastewater for production chemicals for the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.